Cloud Computing: Empowering the Digital Age with Infinite Possibilities
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, cloud computing has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the way individuals, businesses, and governments access and utilize computing resources. With the rise of the internet and advancements in virtualization and distributed computing, cloud computing has become a dominant paradigm that offers unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. This article explores the concept of cloud computing, its key components, benefits, challenges, and its profound impact on various sectors of society.
- Understanding Cloud Computing:
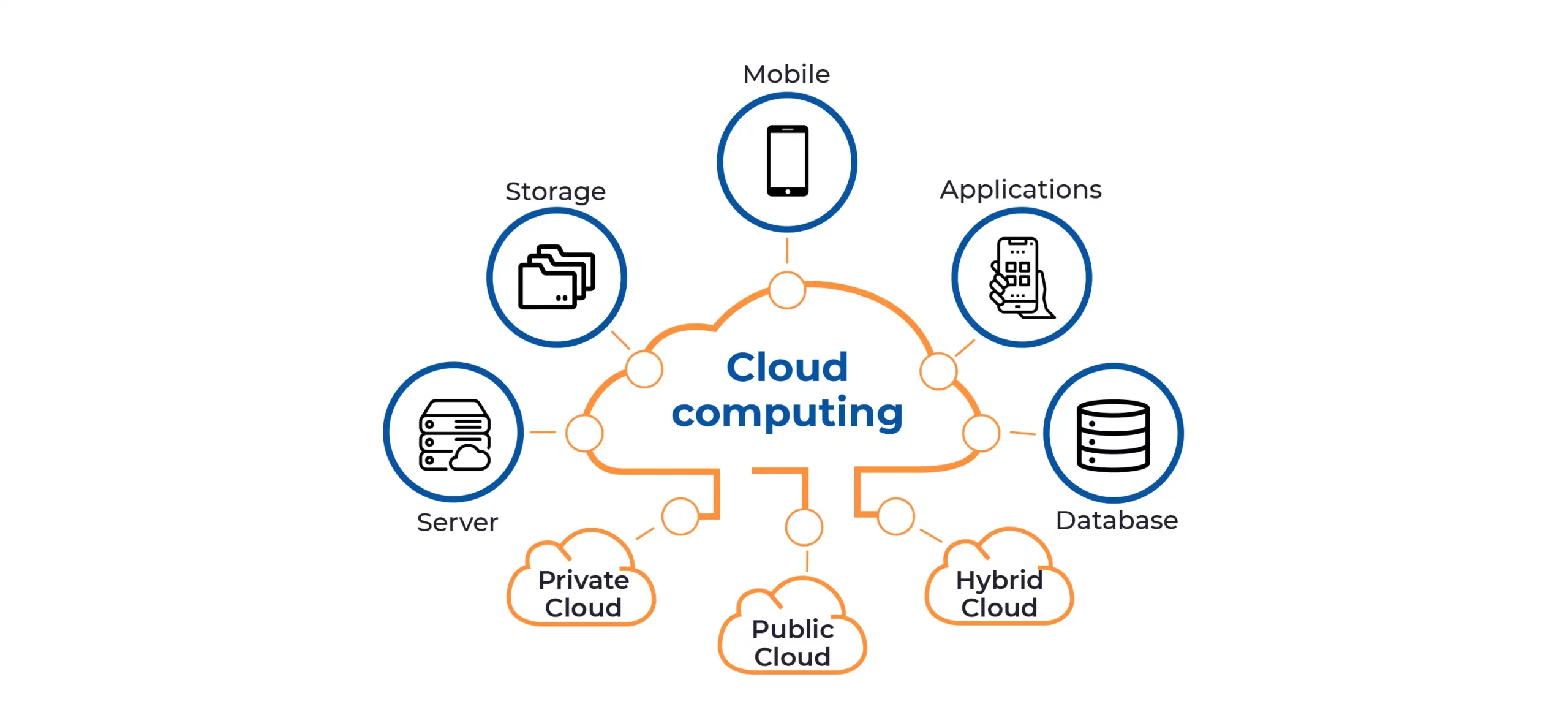
Cloud computing is a model for delivering on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources over the internet. These resources encompass computing power (CPU, memory), storage, databases, software applications, and various services. Cloud service providers operate vast data centers worldwide, allowing users to access these resources remotely via the internet. The fundamental characteristics of cloud computing include:
a) On-Demand Self-Service: Users can provision and manage computing resources autonomously without the need for human intervention from the service provider.
b) Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over standard internet protocols and can be accessed through various devices, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
c) Resource Pooling: Multiple users share the same physical resources in a multi-tenant model, ensuring efficient resource utilization and cost savings.
d) Rapid Elasticity: Cloud resources can be rapidly scaled up or down to accommodate fluctuating workloads and demand spikes.
e) Measured Service: Cloud usage is metered, enabling pay-as-you-go pricing models based on actual consumption.
- Types of Cloud Computing Services:
Cloud computing offers a range of services to cater to diverse requirements:
a) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can access and manage virtual machines, storage, and networking components without worrying about the underlying physical infrastructure.
b) Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud. Developers can build, test, and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
c) Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation. Users can access applications through web browsers, and the provider handles maintenance and updates.
d) Function as a Service (FaaS): Also known as Serverless Computing, FaaS allows developers to execute code in response to specific events without managing the server infrastructure. It automatically scales the resources as needed.
- Advantages of Cloud Computing:
a) Cost Savings: Cloud computing reduces capital expenses by eliminating the need for extensive hardware investments. Users pay only for the resources they consume, making it cost-efficient for small businesses and startups.
b) Scalability: Cloud platforms provide virtually unlimited scalability, allowing businesses to adjust resources according to demand fluctuations, ensuring optimal performance during peak times.
c) Flexibility and Mobility: Cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration among teams spread across the globe.
d) Security: Reputable cloud providers implement robust security measures and compliance standards, often offering better security than what most individual organizations can afford.
e) Innovation and Time-to-Market: Cloud computing expedites application development and deployment, allowing organizations to innovate and release products faster to stay competitive in the market.
- Challenges and Concerns:
Despite its many advantages, cloud computing presents some challenges and concerns:
a) Security and Privacy: Entrusting sensitive data to third-party cloud providers raises concerns about data breaches, data access controls, and data sovereignty.
b) Downtime and Reliability: Cloud outages can disrupt services for extended periods, impacting businesses that rely heavily on cloud infrastructure.
c) Data Migration and Vendor Lock-in: Migrating data to and from different cloud providers can be complex and may result in vendor lock-in, limiting flexibility.
d) Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding data storage and privacy, making compliance a complex task for global cloud users.
- Cloud Computing in Business:
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate and innovate:
a) Digital Transformation: Cloud technology has facilitated the digital transformation of businesses by enabling the adoption of new technologies like AI, IoT, and Big Data analytics.
b) Cost-Effective Scaling: Businesses can scale their operations without incurring significant capital expenses, adapting quickly to